In today’s lesson we discuss the topic of Hexadecimal numbers, and why they are important. As discussed previously, digital devices are nothing more than an incredibly large number of simple on/off switches connected together in clever ways to achieve useful functions. Since there is a need to represent numbers using only on/off switches, the binary number system is used. A switch that is in the on condition can be thought of as a “1” while a switch in the off condition can be thought of as a “0”. by stacking these switches side by side, we can represent almost any number by simply working with enough switches. As things got more complex, and the number of switches increased, it became untenable to keep up with all the 0’s and 1’s. Hence, groups of 4 switches were bunched together, and the Hexadecimal system was born. Understand Hexadecimal is simply a way to keep track of switches that is more convenient than the Binary system. This video discusses in detail, and gives lots of examples.
Category Archives: Arduino
Arduino Tutorial 40: Controlling DC Motor Speed and Direction with Pushbuttons
In this lesson we explore how to control the speed and direction of a DC motor using two buttons. We are using the L293D motor controller and a small DC motor for demonstration purposes. We are using parts from our Elegoo Super Stater Kit, which you can get HERE. The basic circuit was explained in Lesson 37, and we are using that work as a starting point. The schematic below will get you started in connecting your circuit. Be sure and connect one of the Arduino ground pins to the ground rail in the second to the bottom row in the diagram below. It is good practice to connect all your grounds together.
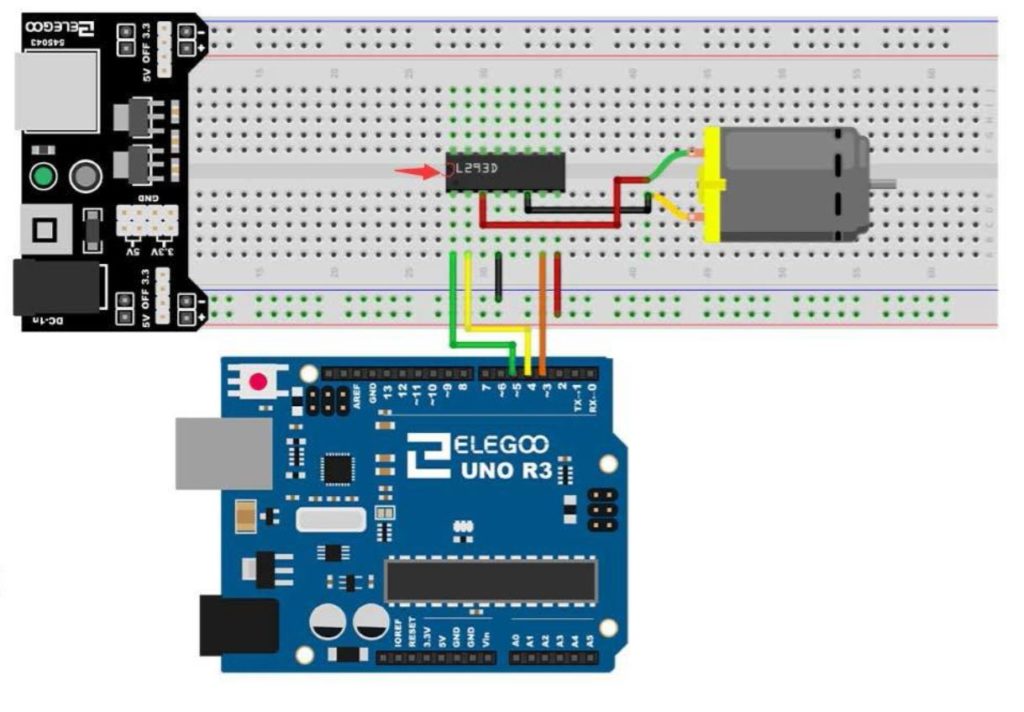
The code we developed in the video lesson is shown below for your convenience.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 | int speedPin=5; int dir1=4; int dir2=3; int BP1=8; int BP2=9; int B1Val; int B2Val; int mSpeed=0; int dt=500; void setup() { // put your setup code here, to run once: pinMode(speedPin,OUTPUT); pinMode(dir1,OUTPUT); pinMode(dir2,OUTPUT); pinMode(BP1,INPUT); pinMode(BP2,INPUT); digitalWrite(BP1, HIGH); digitalWrite(BP2, HIGH); Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: B1Val=digitalRead(BP1); B2Val=digitalRead(BP2); Serial.print("Motor Speed "); Serial.println(mSpeed); if (B1Val==0){ mSpeed=mSpeed-10; delay(dt); } if (B2Val==0){ mSpeed=mSpeed+10; delay(dt); } if (mSpeed>255){ mSpeed=255; } if (mSpeed<-255){ mSpeed=-255; } if (mSpeed==10){ mSpeed=100; } if (mSpeed==-10){ mSpeed=-100; } if (mSpeed==90 || mSpeed ==95){ mSpeed=0; } if (mSpeed==-90 || mSpeed==-95){ mSpeed=0; } if (mSpeed==0){ analogWrite(speedPin,0); } if (mSpeed>0){ digitalWrite(dir1,LOW); digitalWrite(dir2,HIGH); analogWrite(speedPin,mSpeed); } if (mSpeed<0){ digitalWrite(dir1,HIGH); digitalWrite(dir2,LOW); analogWrite(speedPin,abs(mSpeed)); } } |
9-Axis IMU LESSON 18: Visualizing Pitch and Yaw in Vpython
In this lesson we show you how to visualize Yaw and Pitch in Vpython. We create a visual representation of our breadboard, Arduino Nano, and BNO055 and then rotate it in three dimensions with and without pitch. For your convenience, the code we developed in this video are presented below.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 | from vpython import * from time import * import numpy as np import math scene.range=5 toRad=2*np.pi/360 toDeg=1/toRad scene.forward=vector(-1,-1,-1) scene.width=600 scene.height=600 xarrow=arrow(lenght=2, shaftwidth=.1, color=color.red,axis=vector(1,0,0)) yarrow=arrow(lenght=2, shaftwidth=.1, color=color.green,axis=vector(0,1,0)) zarrow=arrow(lenght=4, shaftwidth=.1, color=color.blue,axis=vector(0,0,1)) frontArrow=arrow(length=4,shaftwidth=.1,color=color.purple,axis=vector(1,0,0)) upArrow=arrow(length=1,shaftwidth=.1,color=color.magenta,axis=vector(0,1,0)) sideArrow=arrow(length=2,shaftwidth=.1,color=color.orange,axis=vector(0,0,1)) bBoard=box(length=6,width=2,height=.2,opacity=.8,pos=vector(0,0,0,)) bn=box(length=1,width=.75,height=.1, pos=vector(-.5,.1+.05,0),color=color.blue) nano=box(lenght=1.75,width=.6,height=.1,pos=vector(-2,.1+.05,0),color=color.green) myObj=compound([bBoard,bn,nano]) while (True): pitch=45*toRad for yaw in np.arange(0,2*np.pi,.01): rate(50) k=vector(cos(yaw)*cos(pitch), sin(pitch),sin(yaw)*cos(pitch)) y=vector(0,1,0) s=cross(k,y) v=cross(s,k) frontArrow.axis=k sideArrow.axis=s upArrow.axis=v myObj.axis=k myObj.up=v sideArrow.length=2 frontArrow.length=4 upArrow.length=1 |
9-Axis IMU LESSON 17: Review of Basic Trigonometry
In this video we review the basic trigonometry needed in order to get the Vpython visualization to work. With this quick trig tutorial, you should have the math you need to finish the project.
Arduino Tutorial 39: Using a Joystick to Control DC Motor Speed and Direction
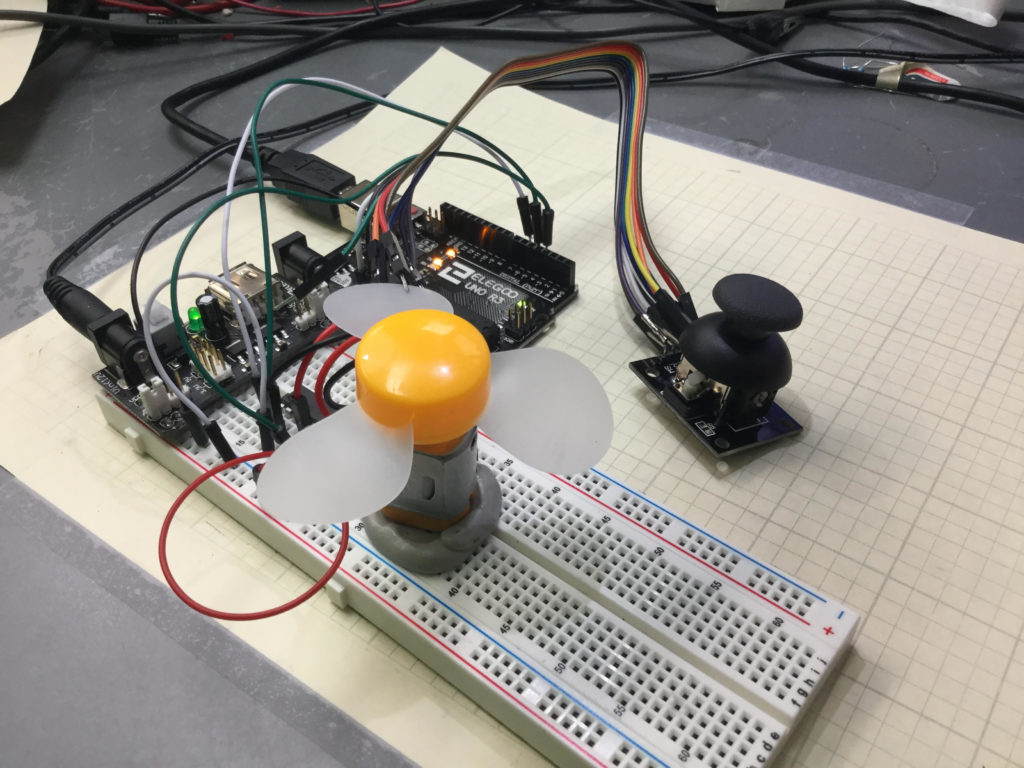
Lesson 37 and 38 showed some preliminary concepts in controlling a DC motor using an arduino and the L293D motor controller. In the video above we show how to control the speed and direction of a simple DC motor using a joystick. In the neutral position, the motor is stationary. Then the speed smoothly increases as you move the joystick forward, until you reach maximum speed.
Lesson 37 and 38 showed some preliminary concepts in controlling a DC motor using an arduino and the L293D motor controller. In the video above we show how to control the speed and direction of a simple DC motor using a joystick. In the neutral position, the motor is stationary. Then the speed smoothly increases as you move the joystick forward, until you reach maximum speed. Similarly, in pulling the joystick back from the neutral position, the motor gradually increases speed in the reverse direction. The diagram below shows the basic motor control schematic we are working from.

In the circuit diagram above, we also add a wire to connect the arduino ground to the power supply ground. It is always good to have all components connected to a common ground rail. Of course, you also need to add the joystick controller as shown in the video.
This is the code we used in this
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | int speedPin=5; int dir1=4; int dir2=3; int mSpeed; int jPin=A1; int jVal; void setup() { // put your setup code here, to run once: pinMode(speedPin,OUTPUT); pinMode(dir1,OUTPUT); pinMode(dir2,OUTPUT); pinMode(jPin,INPUT); Serial.begin(9600); } void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: jVal=analogRead(jPin); Serial.println(jVal); if (jVal<512){ digitalWrite(dir1,LOW); digitalWrite(dir2,HIGH); mSpeed=-255./512.*jVal+255.; analogWrite(speedPin,mSpeed); } if(jVal>=512){ digitalWrite(dir1,HIGH); digitalWrite(dir2,LOW); mSpeed=(255./512.)*jVal-255.; analogWrite(speedPin,mSpeed); } } |
